the following data are for falling head permeability test|falling head permeability test lab report : wholesalers The falling head method of determining permeability is used for soil with low discharge, whereas the constant head permeability test is used for coarse-grained soils with a reasonable .
24 de nov. de 2023 · Newcastle e Chelsea medem forças neste sábado (25), pela 13ª rodada da Premier League.Enquanto os Magpies ocupam a 7ª colocação do campeonato, os Blues estão apenas na 10ª.As duas equipes .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 30 de mai. de 2023 · Nesta quarta-feira, 31, às 16 horas (horário de Brasília), Sevilla e Roma se enfrentam na Puskas Arena, em Budapeste, na Hungria, pela final da Liga Europa. . Pesquisar por Jogadores. 333 447 .
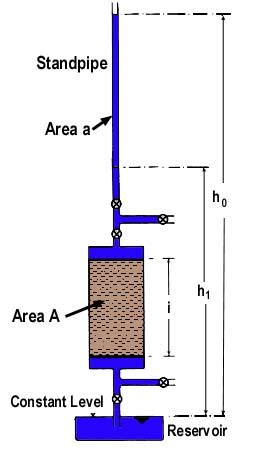
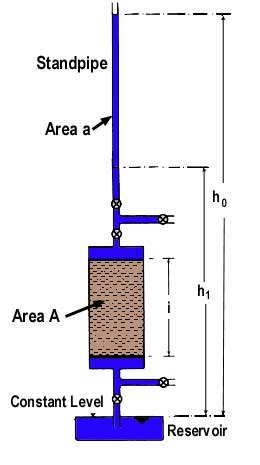
See Answer. Question: The following data are for a falling-head permeability test: Length of the soil sample = 140 mm Diameter of soil sample = 70 mm Area of the standpipe = 19.6 mm^2 At time t = 0, head difference = 500 mm At time t = 7 min, head difference = 350 mm a. .Question: The following data are for a falling-head permeability test: - Length of the soil sample: 150 mm - Area of the soil sample: 1,964 mm2 - Area of the standpipe: 25 mm2 - At time t=0 .
Textbook: Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (9th Edition). Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan, Cengage learning, 2018.Chapter-by-Chapter Playlists (including a. This video shows how to perform a falling head permeability test for fine-grained soil. This test is typically performed on fine-grained soil with low permea.For a falling or variable head permeability test, the following are given: Length of soil specimen = 12 cm Cross sectional area of standpipe = 0.018 sq. cm. Diameter of soil specimen = 7.5 cm .The falling head method of determining permeability is used for soil with low discharge, whereas the constant head permeability test is used for coarse-grained soils with a reasonable .
falling head permeability test standard
falling head permeability test pdf
A falling-head permeability test is to be performed on a soil whose permeability is estimated to be 2.8 × 1 0 − 6 m / s 2.8 \times 10^{-6} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s} 2.8 × 1 0 − 6 m / s. What .
During a falling-head permeability test, the head fell from 49 to 28 cm in 4.7 min. The specimen was 8 cm in diameter and had a length of 85 mm. The area of the standpipe was 0.45 \mathrm .Variable head permeability test is one of several techniques by which the permeability of soil is determined. It is used to evaluate the permeability of fairly less previous soil. Permeability is the measure of the ability of soil to allow .
falling head permeability test lab report
PROBLEM 1 The following data are for a falling-head permeability test: Length of the soil sample = 500 mm Area of the soil sample = 1600 mm2 Area of the standpipe = 97 mm2 At time t = 0, head difference = 410 mm At time t = 10 .Permeability of a coarse grained soil can be determined by a constant head permeability test (AS1289.6.7.1-2001; ASTM D2434), and in a fine grained soil, falling head permeability test (AS1289.6.7.2-2001; ASTM D5856) works the best. In a constant head permeability testThe test is initiated after the vacuum saturation of the sample with deaired water. Readings for time, head (water levels in the manometer tubes), and quantity of flow under intervals of increasing head pressures determine final results. .For a falling head permeability test, the following are given: length of specimen is 360 mm, area of specimen is 70 cm2 , and hydraulic conductivity of soil specimen is 0.165 cm/min. what should be the area of the stand pipe for the head to drop from 700cm to 360cm in 7 mins? compute the seepage velocity under the test condition if the soil specimen has a void ratio of .
falling head permeability test formula
There are two general types of permeability test methods that are routinely performed in the laboratory: (1) the constant head test method, and (2) the falling head test method. The constant head test method is used for permeable soils (k>10-4 cm/s) and the falling head test is mainly used for less permeable soils (k<10-4 cm/s).The falling head method of determining permeability is used for soil with low discharge, whereas the constant head permeability test is used for coarse-grained soils with a reasonable discharge in a given time. For very fine-grained soil, capillarity permeability test is recommended. Usually, permeability of soils is determined by two methods: 1.Find step-by-step Engineering solutions and the answer to the textbook question The following data are for a falling-head permeability test: - Length of the soil sample =140 mm - Diameter of soil sample =70 mm - Area of the standpipe =19.6 mm$^2$ - At time t=0, head difference =500 mm - At time t=7 min, head difference =350 mm a. Determine the hydraulic conductivity of the .The following data are for a falling-head permeability test: Length of the soil sample = 150 mm Area of the soil sample = 1964 mm^2 Area of the standpipe = 25 mm^2 At time t = 0, head difference = 400 mm At time t = 8 min, head difference = 200 mm a. Determine the hydraulic conductivity of the soil (cm/sec). b.
FIELD MANUAL 110 Table 17-1.—A glossary of abbreviations and definitions used in permeability calculations K = Coefficient of permeability in feet (meters) per year under a unit gradient. Q = Steady flow into the well in ft3/sec [m3/sec]. H = The effective head of water in the well in feet (m). For packer tests, determining the effective head is definedThe following data are for a falling-head permeability test: Length of the soil sample = 500 mm; Area of the soil sample = 1600 mm:; Area of the standpipe 97 mm:; At time = 0, head difference 410 mm; At time t 10 minutes, head difference = 185 mm.Variable head permeability test is one of several techniques by which the permeability of soil is determined. . after selecting the suitable initial and final heads, h1, and h2, respectively, observe the time intervals for the head to fall from h1 to (h1*h2)^0.5, and similarly from (h1*h2)^0.5 to h2. . Data Sheet . The following values .
Question: Problem 3 The following data are for a falling-head permeability test: Length of the soil sample = 140 mm • Diameter of soil sample = 70 mm • Area of the standpipe = 19.6 mm • At time t = 0, head difference = 500 mm • At time t = 7 min, head difference = 350 mm a. Determine the hydraulic conductivity of the soil (cm/sec) b.The following data are for a falling-head permeability test: Length of the soil sample = 140 mm Diameter of the soil sample = 70 mm Area of the stand pipe = 19.6 mm² At time t=0, head difference = 500 mm At time t = 7 minutes, head difference = 350 mm (i) Determine the hydraulic conductivity of the soil (m/sec) What was the head difference at t = 5 minutes?
falling head permeability method
The following data are for a falling-head permeability test: • Length of the soil sample = 150 mm • Area of soil sample = 1964 mm^2 • Area of the standpipe = 25 mm^2 • At time t = 0, head difference = 400 mm • At time t = 8 min, head difference = 200 mm a. Determine the hydraulic conductivity of the soil (cm/sec). (ans. 2.75x10^-4 cm/s)
bedienungsanleitung burg wächter feuchtigkeitsmessgerät
For a falling or variable head permeability test, the following are given: Length of soil specimen = 12 cm Cross sectional area of standpipe = 0.018 sq. cm. Diameter of soil specimen = 7.5 cm Time of collection of water = 65 sec Head difference at time t = 0; = 70 cm Head difference at time t = 65; = 40 cm Temperature of water = 17 ° C Find .Question: 7.8 The following data are for a falling-head permeability test: • Length of the soil sample = 140 mm • Diameter of soil sample = 70 mm • Area of the standpipe = 19,6 mm? • At time t = 0, head difference = 500 mm • At time t = 7 min, head difference = 350 mm a. Determine the hydraulic conductivity of the soil (cm/sec) b.
The following data are for a falling-head permeameter test: Length of the soil sample = 140mm Diameter of soil sample = 70 mm Area of the standpipe = 19.6 mm2 At time t = 0, head difference = 500 mm At time t = 7 min, head .
bedienungsanleitung lux feuchtigkeitsmessgerät
Question: Problem 5) (20 pts) A falling-head permeability test gave the following data: Length of soil sample= 400 mm Area of soil sample= 1500 mm2 Area of standpipe= 92 mm2 . At time t=0, head difference=400 mm ) At time t=15 min, head difference= 200 mm KN The test was conducted at 20°C where yw = 9.789 = m3 S η = 1.005 * 10-3 N * m2 a.The following data are for a falling-head permeability test:• Length of the soil sample = 140 mm• Diameter of soil sample = 70 mm• Area of the standpipe = 19.6 mm2• At time t = 0, head difference = 500 mm• At time t = 7 min, head difference = 350 mma.The following data are for a falling- head permeability test: • Length of the soil sample = 400 mm Area of the soil sample 7854 mm2 %3D Diameter of the standpipe 11 mm %3D At time t = 0, head difference = 450 mm At time t = 8, head difference 200 mm If the test was conducted at 20°C at which yw =9.789 kN/m' and n = 1.005 x 10³N s/m2, a.
(15 pts) The following data are for a falling-head permeability test: • Length of the soil sample = 170 mm Area of the soil sample = 1975 mm² Area of the standpipe = 32 mm? At t= 0, head difference = 440 mm • At t= 8 min, head difference = 222 mm Determine: a. Hydraulic conductivity of the soil (cm/sec). b. Head difference at t = 5 min. .
Concept: Falling head permeability test or variable head permeability test Coefficient of permeability, \(\rm{k = \frac{{2.303 \times a \times L}}{{A \times t. . Select the option that is correct regarding the following two statements, labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R), with respect to permeability of soil. Assertion (A): Permeability .For a falling-head permeability test, the following values are given: Length of specimen = 8 cm, Area of soil specimen = 1.6 cm2, Area of standpipe = 0.06 cm2, Head difference at time (t = 0)= 20 cm, Head difference at time (t = 180 sec) = 12 cm. Determine the hydraulic conductivity of the soil. a. 0.0235 cm/sec b. 0.000852 cm/sec c. 1.852 cm/sec d. 0.0025 cm/secA rising head test (Figure 12.7b) is the converse of a falling head test. It involves rapidly removing water from the borehole and observing the rate at which water rises in the borehole. The test does not need a water supply (which can be an advantage in remote locations) but does require a means of removing water rapidly from the borehole.In a falling head permeability test, the following data was obtained: diameter of standpipe = 1.5 cm; diameter of sample = 10.16 cm; height of water level at beginning of test (h1) = 30 cm; length of sample (L) = 20 cm. The soil had a coefficient of permeability (k) equal to 3.4 x .
The falling head permeability test was run on a soil sample 9.6 cm in diameter and 10 cm long. The head at the start of the test was 90 cm. The coefficient of permeability of the soil was found to be 5x10^-6 cm/sec, the diameter of the standpipe was 1 cm. a) Determine the flow at the start of the test (cm^3/hr). b) Determine how much head was lost during the first 30 minutes.Textbook: Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (9th Edition). Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan, Cengage learning, 2018.Chapter-by-Chapter Playlists (including a.
besser wie jeder hygrometer feuchtigkeitsmessgerät
bosch feuchtigkeitsmessgerät für mauerwerk
WEBolha como ficou fofo nosso bolo todo feito em chantilly.quer aprender? comenta que faço o vídeo ensinando..sou iniciante ainda mas teremos muita novidade a.
the following data are for falling head permeability test|falling head permeability test lab report